Boils & Abscesses
ChatRx uses advanced AI to accurately diagnose the symptoms of boils and abscesses prescribe medications when necessary.
Overview
A boil, also known as an abscess, is a localized skin infection that typically begins as a painful, red lump on the skin.
Boils are caused by the Staphylococcus aureus bacteria and can occur anywhere on the body, but are most common in areas with hair follicles or sweat glands.
If you have a painful skin abscess, consider starting a quick symptom assessment using our online infection care telemedicine platform.
AI-Powered Symptom Assessment Coming in Spring 2025!
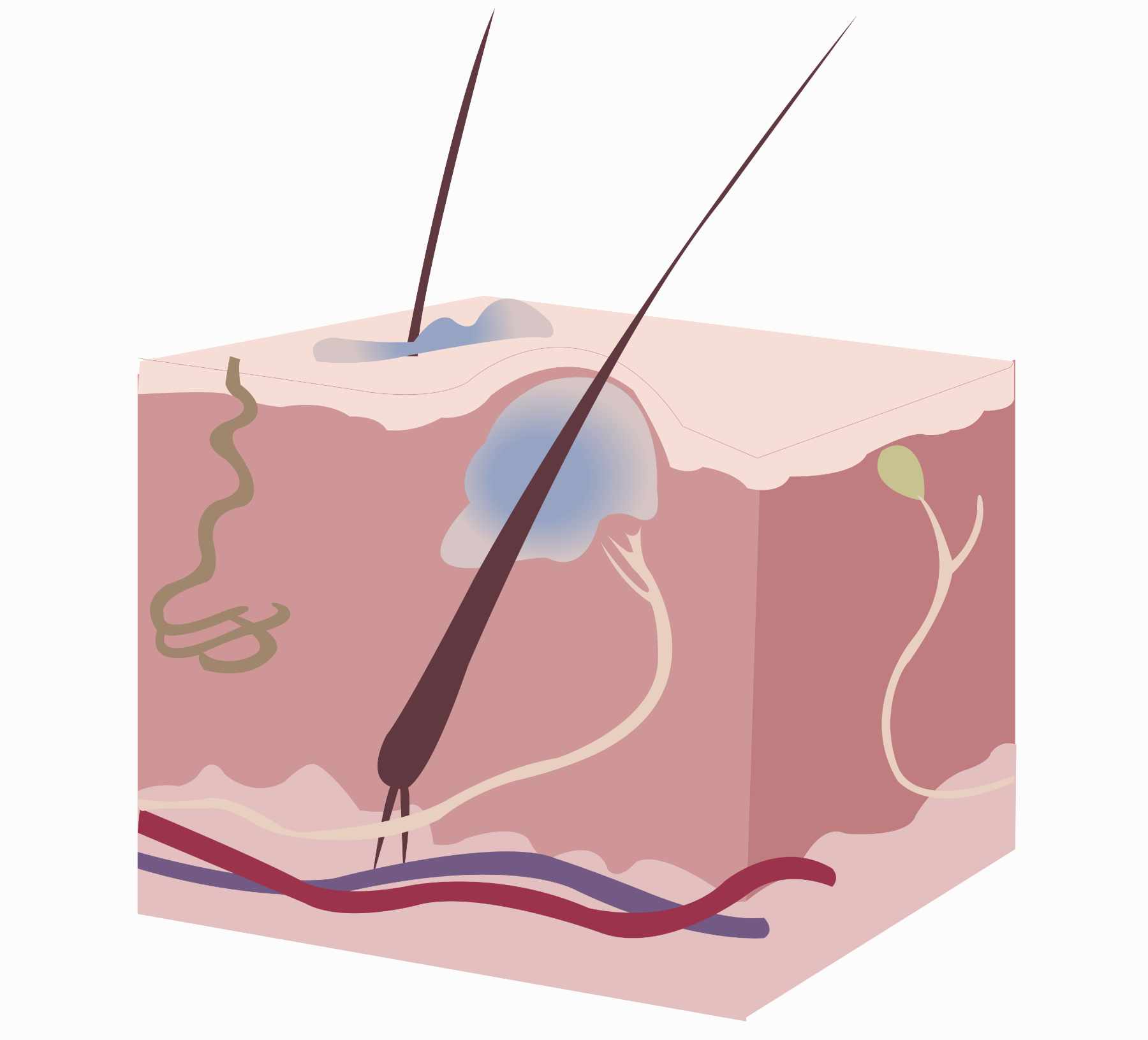
What are Boils?
- Localized skin infections that start as painful, red lumps
- Caused by the Staphylococcus aureus bacteria
- Can occur anywhere on the body, but are most common in areas with hair follicles or sweat glands
- Often start as small, red bumps that gradually grow larger and more painful
Causes of Boils
- Infection with the Staphylococcus aureus bacteria
- Clogged hair follicles or sweat glands that provide an environment for bacterial growth
- Weak immune system or underlying medical conditions that increase susceptibility
- Skin injuries or irritation that allow the bacteria to enter the skin
Preventing Boils
- Practice good personal hygiene, including regular handwashing
- Avoid touching or picking at the skin, as this can introduce bacteria
- Wear loose, breathable clothing to reduce skin irritation and sweating
- Maintain a healthy immune system through a balanced diet and regular exercise
- Promptly treat any minor skin injuries or infections to prevent them from worsening
Painful Skin Condition?
AI-Powered Boils & Abscesses Treatment Coming This Spring!
Start Your Skin Condition Assessment Now
Symptoms of Boils
- A painful, red lump on the skin that gradually grows larger
- Pus or fluid-filled head on the boil
- Redness, swelling, and warmth around the affected area
- Fever or other signs of infection in severe cases
Treating Boils
- Warm compresses to help bring the boil to a head and drain the pus
- Over-the-counter pain relievers to manage discomfort
- Topical antibacterial ointments to help fight the infection
- Prescription-strength antibiotics for severe or recurrent boils
Self-Care for Boils
- Apply warm compresses several times a day to help the boil drain
- Avoid touching or picking at the boil, as this can spread the infection
- Keep the affected area clean and avoid sharing personal items
- Monitor the boil for signs of worsening, such as increased pain or redness
Feeling Unwell?
AI-Powered Symptom Assessment Coming in Spring 2025!
Antibiotics for Boils
- Topical antibacterial ointments, such as mupirocin, can help fight the infection
- Oral antibiotics, like cephalexin or dicloxacillin, may be prescribed for severe or recurrent boils
- Proper use of antibiotics is important to prevent the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria
Risk Factors for Boils
- Weakened immune system due to underlying medical conditions or medications
- Poor personal hygiene or skin irritation that allows bacteria to enter the skin
- Shared use of personal items, such as towels or clothing, with an infected individual
- Exposure to environments with a high concentration of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria
Summary
Boils, or abscesses, are common skin infections that can be effectively managed with the right care and treatment. By practicing good hygiene, avoiding skin irritation, and seeking prompt medical attention when necessary, individuals can reduce the risk of developing boils and minimize the impact of this condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
A boil typically starts as a tender, red bump that becomes increasingly painful and swollen over days. Unlike pimples, boils grow larger and develop a white or yellow pus-filled center. They’re also usually more painful than other skin bumps. Not sure what that painful skin bump is? Get an instant online assessment through ChatRx’s AI doctor platform.
Yes, the bacteria in the pus can spread and cause new infections. Never squeeze or pop a boil. If it drains naturally, immediately clean the area with antiseptic and dispose of all cleaning materials carefully. Keep the area covered with a sterile bandage.
Warm compresses provide the most relief and help bring the boil to a head. Apply them 3-4 times daily for 10-15 minutes. Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can also help manage the pain and reduce inflammation. Have a painful skin abscess that’s not improving? Skip the waiting room – get an immediate evaluation through ChatRx’s AI-powered medical platform.
Recurring boils can indicate bacterial colonization in your body or a weakened immune system. Areas with hair, friction, or sweating are particularly vulnerable. Some medical conditions like diabetes can also increase your risk.
Despite popular online advice, toothpaste, garlic, and other home remedies aren’t proven effective and might irritate your skin further. Stick to warm compresses and proper wound care. Dealing with stubborn or recurring boils? Let our AI doctor assess your symptoms and provide immediate treatment guidance.
If the boil is small and can be kept completely covered, you can continue normal activities. However, avoid activities that cause sweating or friction in the affected area. Stay home if you have fever or the boil is draining.
Seek immediate medical care if the boil is on your face, spine, or groin area, grows larger than 2 inches, comes with fever, or if you have multiple boils. Also watch for red streaks extending from the boil, which could indicate spreading infection.
Most boils take 1-2 weeks to heal completely. With proper care, they usually come to a head within 4-7 days and begin draining naturally. Larger boils or those treated with antibiotics might take longer to resolve fully.